The Energy Efficiency Certificate is a document required by the Ministry of Industry, Energy, and Tourism for all homes that are going to be rented or sold to another person. This measure aims to promote energy efficiency improvement in all European Union countries by providing information about energy consumption and CO2 emissions of a property that is advertised for sale or rent.
Energy Efficiency Certificates are not only applied to homes but also to appliances based on their consumption and performance per unit of energy consumed. The energy certificate is an essential requirement for selling or renting any type of property.
In Spain, the energy efficiency certificate has been mandatory since 2013 to put a property up for sale or rent. This measure was implemented with the purpose of improving energy efficiency in the construction of new properties and promoting more responsible energy use. The regulation of energy efficiency certificates in Spain is found in Royal Decree 390/2021, a regulation created to comply with the European directive on energy efficiency and reduction of CO2 emissions in member states.
Failure to comply with this regulation can result in fines ranging from €300 to €6,000 for minor infractions, €601 to €1,000 for serious infractions, and €1,001 to €6,000 for very serious infractions.
How Does the Energy Efficiency Certificate Work?
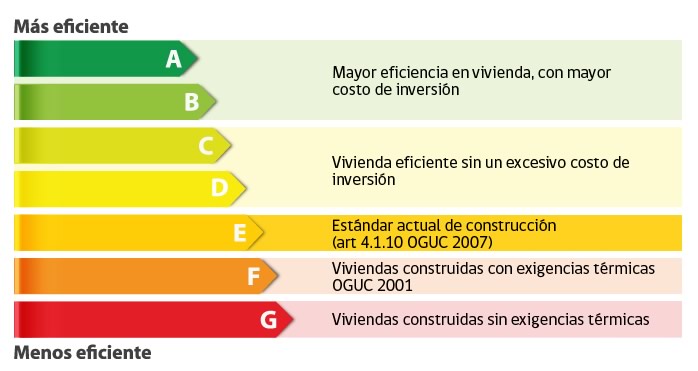
The Energy Efficiency Certificate serves as a tool that provides information about the energy efficiency of a property, whether it's a home, a building, or an appliance. This certificate is issued after an evaluation conducted by a specialized technician and is presented in the form of an energy label, which includes a rating and other relevant data. Here are the different ratings found on the energy label:
- Energy Rating (Letters A to G): The rating is represented on a letter scale ranging from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient). The letter A indicates a high level of energy efficiency, meaning the property consumes less energy and is more environmentally friendly. Conversely, letter G indicates low energy efficiency and higher energy consumption.
- Color Coding: In addition to letters, the energy label often uses a color code, where A is represented in green (indicating efficiency), and as the rating decreases, the colors shift towards red (indicating lower efficiency).
- Annual Energy Consumption: The certificate also provides information about the annual energy consumption of the evaluated property. This allows users to estimate how much energy the property will consume in a year and, therefore, plan their consumption more efficiently.
- CO2 Emissions: The certificate includes data on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions associated with the property's energy consumption. This helps property owners and buyers understand the environmental impact of the property and its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.

Impact on Home Energy Efficiency
Having an energy-efficient home equipped with equally efficient appliances can result in significant savings. According to experts from iAhorro, a 70-square-meter home with an E energy rating (the most common home profile in Spain) has an estimated energy consumption of around €735 per year.
Improving the energy efficiency of the home to achieve a B rating would reduce this bill to around €282 per year. Additionally, these same experts calculate that annual spending on energy consumption of appliances amounts to approximately €990. Despite the higher initial investment in the purchase of energy-efficient appliances compared to less efficient ones, this investment pays off over time by saving energy and reducing future electricity bills.
At Marbellous Estates, we consider energy efficiency as an advancement in both consumer savings and environmental preservation. Some of the key recommendations to make our home spending more affordable include:
- Adjusting the contracted electrical power to actual electricity consumption needs.
- Investing in insulation materials that protect homes from cold in winter and keep them cool in summer, saving heating and air conditioning costs in the medium term.
- Replacing inefficient boilers, which consume large amounts of energy for many hours, with more modern and efficient models. This can result in up to a 25% annual heating cost savings.